Battery Life
This is measured in number of discharge/charge cycles rather than years. The more deeply the battery is discharged the lower the number of cycles it will last for.
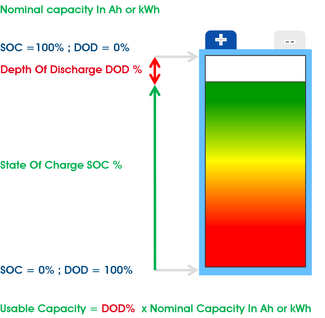
The percentage depth of discharge (DOD) of a battery means how much of the available energy in the battery is used before recharge.
Usually expected battery lifetime is given as a number of cycles to a stated DOD.
Although deep cycle lead-acid batteries typically can be discharged by 80% of their rated capacity (80% DOD); designing for less than 50% gives much longer battery life.
Most lithium-ion batteries can be discharged to around 80% of nominal capacity without significant effect on lifetime.
To ensure long lifetime batteries should be cared for and any required maintenance carried out when needed.
Battery Efficiency
No battery is 100% efficient. Energy is lost in storage, charging and discharging. Its efficiency is a measure of energy loss in the entire discharge/recharge cycle.
eg. For an 80% efficient battery, for every 100kWh put into the battery, only 80kWh can be taken out.
With new lead acid batteries efficiencies of ~ 80 - 90% can be expected, however this decreases with use, age, sulphation and stratification.
Lithium Ion batteries have typical efficiencies of over ~ 95%
To maximise efficiency, batteries should be kept at room temperature, and sized correctly for their purpose, both to minimise self discharge, and to prevent them being charged and discharged too rapidly.
Battery Care

The battery bank should be installed, preferably on its own, in a weather & frost protected, well ventilated shed or other enclosed area. Ideal temperature is ~ 20 ºC and should not be more than 43 ºC.
- For optimum performance, batteries should all be of the same brand, age and amp-hour capacity within a battery bank.
- Proper battery connections should be used, designed for high currents & long life. Connections should be tight and covered with petroleum jelly to prevent corrosion.
- Batteries produce explosive hydrogen gases during charging, so avoid sparks or flames. They contain corrosive chemicals.
- Utmost care must be taken whilst working with batteries.
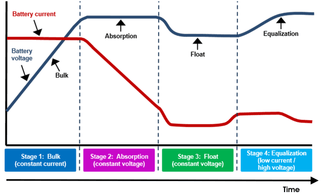
Maintenance requirements vary by battery chemistry and configuration. Additionally, some maintenance tasks, such as adding water or equalization, require on-site manual operations and/or oversight, while charge regulation, voltage checks and related measurements can be automated via sophisticated charge controllers or battery management systems, which are a de facto requirement for lithium-ion batteries.
Lead acid batteries
Sealed lead-acid batteries, gel cells and AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat), are often referred to as maintenance-free because they don’t require watering or an equalisation charge. This makes them well-suited for remote or unattended power systems. However, sealed batteries require accurate regulation to prevent overcharge and over-discharge.
Lead-acid batteries should always be recharged as soon as possible. The positive plates change from lead oxide, when charged, to lead sulfate, when discharged. The longer they remain in the lead sulfate state, the more of the plate remains lead sulfate when the battery is recharged. The portion of the plates that become “sulfated” can no longer store energy. Batteries that are deeply discharged and then only partially charged on a regular basis often fail in less than one year. Always use temperature compensation when charging batteries to prevent over or under-charging.
NOTE: Battery warranties do NOT cover damage due to poor maintenance or loss of capacity from sulfation.
Check the electrolyte level in wet-cell, or “flooded” batteries, at least once every 3 months and top-off each cell with distilled water. Keep the tops of batteries clean and check that cables are tight.
Lithium batteries
These are usually maintenance free. However, to ensure correct operation all connections should be checked periodically and tightened to correct torque values where necessary as temperature variations can cause them to loosen.
Any monitoring or BMS software should be used to check for any irregularities in operation.